KIP 163: CnStakingV3 with public delegation
| Author | Lewis, Ian, Ollie, and Aidan |
|---|---|
| Discussions-To | https://github.com/klaytn/kips/issues/163 |
| Status | Final |
| Type | Core |
| Created | 2024-04-30 |
Simple Summary
Introducing a new CnStakingV3 with public delegation.
Abstract
The new CnStakingV3 will be compatible with public delegation. The public delegation will support delegation and redelegation for general users. Also, the staking information interval will be changed to 1 block, which is currently 86,400 blocks.
Motivation
In KIP-81, Klaytn introduced CnStakingV2. However, it’s difficult for general users to delegate their KLAY if a validator doesn’t provide public delegation services. For example, users can delegate to SwapScanner and KommuneDAO since they provide their own public delegation services. This narrowed the delegation options to a small number of GC members. In addition, Klaytn expects various GC members to join in the merged chain; there is a strong need to introduce a new CnStakingV3 with public delegation.
The redelegation can make massive staking changes in a short period, which can lead to non-negligible errors in the validator set and reward distribution with the current 86,400 blocks interval. To prevent this, the staking information interval will be changed to 1 block.
Specification
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119.
Overview
CnStakingV3 is basically an upgraded version of CnStakingV2, so it must be compatible with the existing core contracts like AddressBook, StakingTracker and so on. The notifying changes include the following:
-
CnStakingV3 supports public delegation natively, allowing it to receive delegations and re-delegation from general users.
-
Re-delegation is supported between CnStakingV3 enabling public delegation and re-delegation.
A GC member can enable public delegation from CnStakingV3. If it is enabled, all staking functionalities must be proxied via a public delegation contract defined in this proposal, namely PublicDelegation. When users want to delegate their KLAY, they stake KLAY to PublicDelegation and receive shares in return, which represent users’ assets.
PublicDelegation shall be implemented based on an interest-bearing token model, especially ERC-4626. However, shares must not be transferable.
From FORK_BLOCK, the staking information for block N will be come from block N-1 instead of CalcStakingBlockNumber(N).
Smart Contracts Overview
This KIP contains upgraded and newly implemented smart contracts. The overall structure is shown in below diagram.
-
CnStakingV3: an upgraded version of CnStakingV2. It can enable public delegation and use re-delegation between CNs enable public delegation.
-
IKIP163: an interface that a public delegation must implement to be compatible with CnStakingV3.
-
PublicDelegation: a public delegation contract provided by Klaytn. Note that it will be only compatible with CnStakingV3.
Henceforth, CnStakingV3 shall be denoted as CNv3, and Public Delegation as PD.
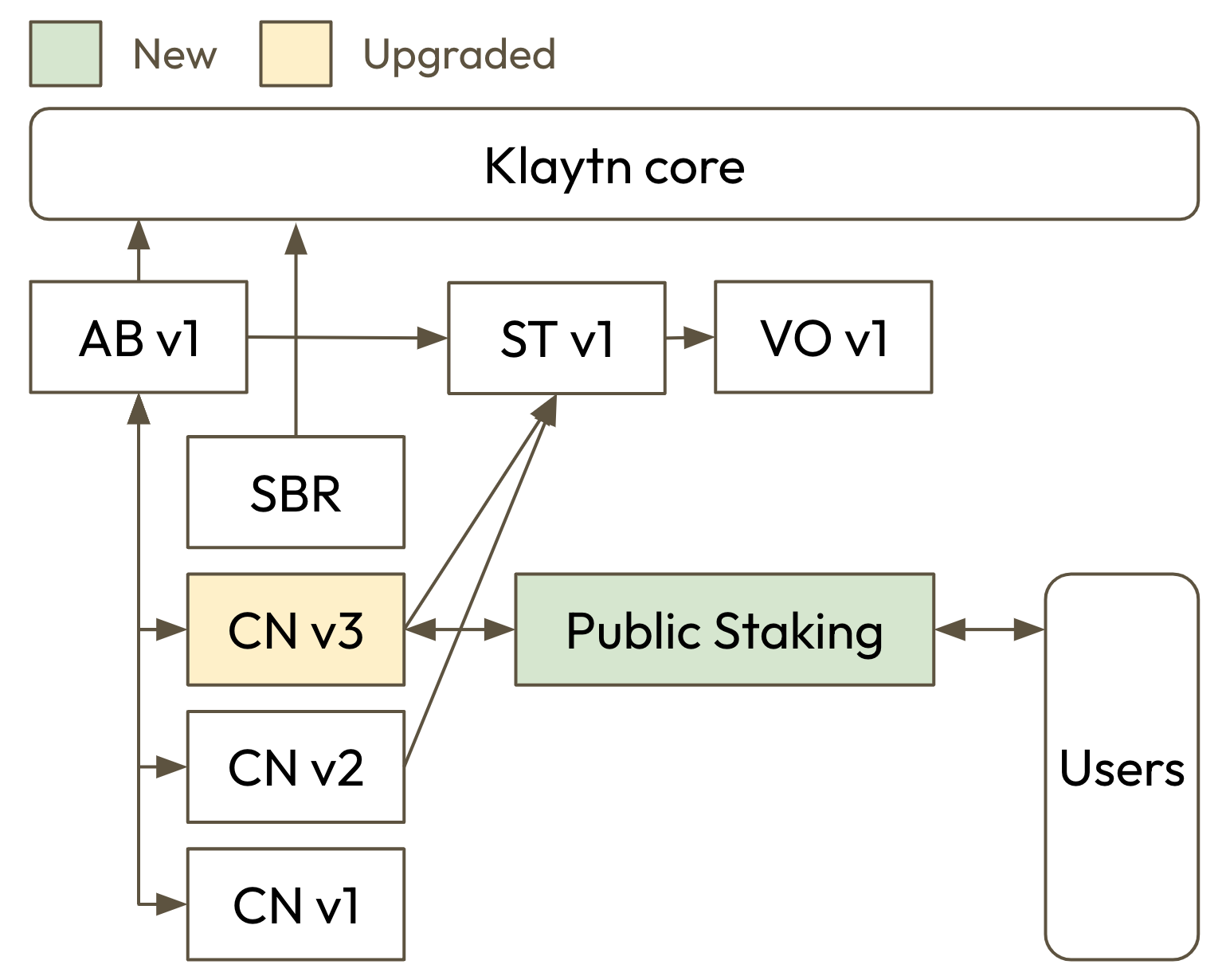
CnStakingV3
CNv3 can use either initial lockup or PD; the two features must be mutually exclusive. If CNv3 uses initial lockup, there’s no difference from CNv2. Henceforth, all CNv3s are considered to be using PD to focus on the newly added features.
Interface
Note that it only addresses changes compared to CNv2. The function delegate renames from stakeKlay to clarify its meaning.
pragma solidity 0.8.25;
interface ICnStakingV3 {
event SetPublicDelegation(address indexed from, address publicStaking, address rewardAddress);
event ToggleRedelegation();
event UpdatePublicStaking(address indexed publicStaking);
event Redelegation(address indexed targetCnStakingV3, address indexed from, address indexed to, uint256 value);
event HandleRedelegation(address indexed prevCnStakingV3, address indexed targetCnStakingV3, address indexed recipient, uint256 value);
// Setup public delegation
function setPublicDelegation(address _pdFactory, bytes memory _pdArgs) external;
// Toggle redelegation
function submitToggleRedelegation() external;
function toggleRedelegation() external;
// Delegation/Redelegation functions.
function delegate() external payable;
function redelegate(address _targetCnV3, address _from, address _to, uint256 _value) external;
function handleRedelegation(address _recipient) external payable;
// Record _account's last redelegation to prevent redelegation hopping.
function lastRedelegation(address _account) external view returns (uint256);
}
Methods
The features added in CNv3 are only active when PD is enabled; without PD, existing features behave exactly as they did in CNv2. If PD is enabled, some staking functions only callable through PD. This ensures that users’ assets staked via PD are safe even if control of CNv3 is compromised.
| PD disabled (Same as CNv2) | PD enabled | |
|---|---|---|
delegate/receive |
No condition | Only PD |
submitApproveStakingWithdrawal |
Only Admin | N.A. |
submitCancelApprovedStakingWithdrawal |
Only Admin | N.A. |
approveStakingWithdrawal |
Only Admin | Only PD |
cancelApprovedStakingWithdrawal |
Only Multi-sig | Only PD |
withdrawApprovedStaking |
Only Multi-sig | Only PD |
The CNv3 must call setPublicDelegation to set public delegation. In setPublicDelegation, it deploys a new public delegation contract and connect to CNv3.
Redelegation can be configured, and it requires that both the originating and the target CNv3 have PD and redelegation enabled to function properly. Users can redelegate their staking to another CNv3 without waiting for lockup period. But to prevent redelegation hopping, which makes Klaytn’s consensus be unstable, users who have been redelegated must wait a lockup period before they can redelegate again. For example, if a user redelegates from [A → B], then user must wait for a lockup period to redelegate from B to another CNv3. The last redelegation records will be stored in each CNv3s. The below diagram shows how redelegation is processed between CNv3 and PD. The action of PD is discussed in more detail in Public Delegation.
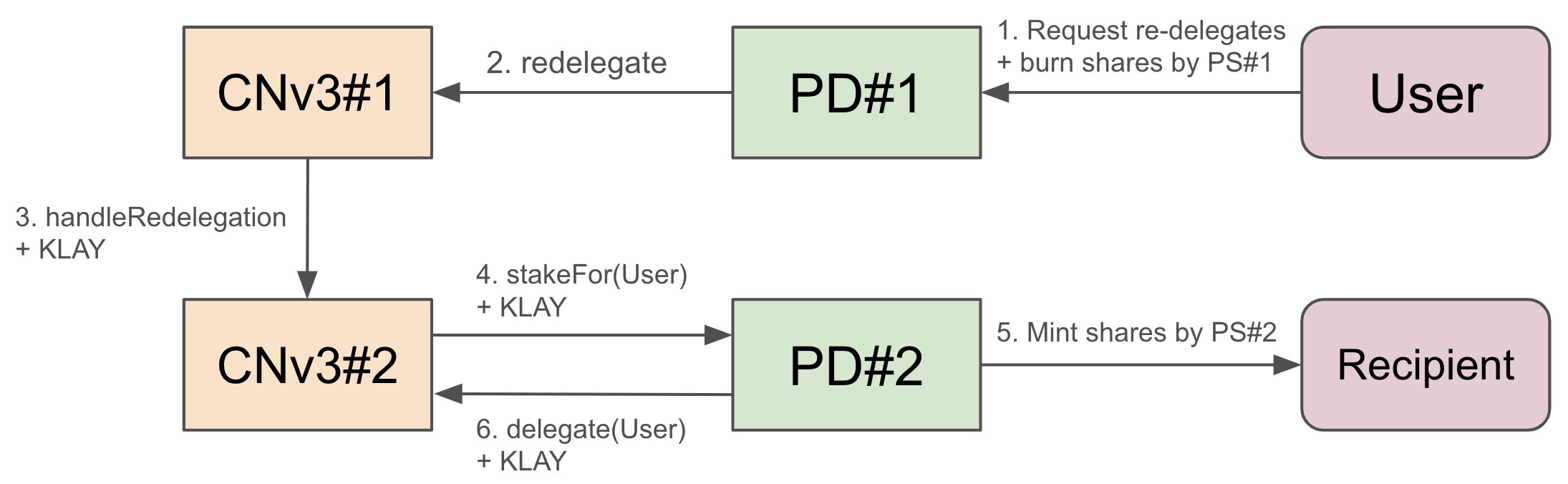
function setPublicDelegation(address _pdFactory, bytes memory _pdArgs);
Deploys and sets a PD to CnV3. The PublicDelegation will be deployed via _pdFactory with _pdArgs. The _pdFactory is a simple factory contract that deploys PublicDelegation, which will be singleton contract deployed by Klaytn. The _pdArgs will be encoded struct PDConstructorArgs to deploy PD. The reward address must be set to the PD address.
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if PD is not enabled.
- The function MUST revert if CnV3 already initialized.
- The function MUST revert if
_pdArgsisn’t encoded correctly. - The function MUST revert if PD deployment fails.
The function emits SetPublicDelegation event.
function redelegate(address _targetCnV3, address _user, uint256 _value);
Requests CNv3 to redelegate _user’s _value of KLAY to _targetCnV3. CNv3 calls handleRedelegation with _value to _targetCnV3 internally.
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if CNv3 does not allow PD, or if the caller is not PD.
- The function MUST revert if CNv3 does not allow redelegation.
- The function MUST revert if
_targetCnV3is itself. - The function MUST revert if
_targetCnV3isn’t a valid CNv3 staking contract registered in AddressBook. - The function MUST revert if
_valueis larger than total staking amount. - The function MUST revert if
lastRedelegation[_user] != 0 && lastRedelegation[_user] + lockup <= block.timestamp.
The function emits Redelegation event.
function handleRedelegation(address _user) payable
Handles redelegation request from departure CNv3. This CNv3 will stake msg.value on behalf of _user using stakeFor(_user) in PD. It allows existing code to be reused without additional implementation for redelegation. It records lastRedelegation[_user] to prevent redelegation hopping.
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if CNv3 does not allow PD.
- The function MUST revert if CNv3 does not allow redelegation.
- The function MUST revert if departure CNv3 isn’t a valid CNv3 staking contract registered in AddressBook.
- The function MUST revert if balance after calling
stakeForis lower than expected.- In
stakeFor, PD will stakemsg.valueback to CNv3. It means CNv3 can compute deterministic balance changes.
- In
The function emits HandleRedelegation event.
IKIP163
IKIP163 must be implemented in PublicDelegation to be fully compatible with CnStakingV3:
Interface
pragma solidity 0.8.25;
/// @title KIP-163 Public Delegation Interface
/// @dev See https://github.com/klaytn/kips/issues/163
interface IKIP163 {
/// @dev Stake KLAY for the _recipient.
/// It is used in CnStakingV3.handleRedelegation to stake KLAY for the _recipient when handling redelegation.
/// It must stake KLAY to the CnStakingV3 in the same transaction.
/// See CnStakingV3.handleRedelegation for more details.
/// @param _recipient The address to stake for
function stakeFor(address _recipient) external payable;
/// @dev Returns the current rewards to be automatically compounded during the `stakeFor` function.
/// It is used in CnStakingV3.handleRedelegation to calculate the expected balance after calling `stakeFor`.
/// If implemented public delegation doesn't support auto-compounding during the `stakeFor`, it should return 0.
/// See CnStakingV3.handleRedelegation for more details.
function reward() external view returns (uint256);
}
Also, all staking operations in CNv3 must be done through public delegation, so there is no fixed interface, but it should call CNv3 appropriately.
Methods
function stakeFor(address _recipient) payable;
It is used in CnStakingV3.handleRedelegation to stake KLAY for the _recipient when handling redelegation. The stakeFor MUST not revert handleRedelegation.
function reward() view returns (uint256);
It returns the current rewards to be automatically compounded during the stakeFor function. It is used in CnStakingV3.handleRedelegation to calculate the expected balance after calling stakeFor function. If the public delegation doesn’t support auto-compounding during the stakeFor, it must return 0, otherwise exact rewards to be compounded. The reward MUST not revert handleRedelegation.
PublicDelegation
PD is a public delegation contract based on ERC4626. It must be set up through setPublicDelegation in CNv3. Since PD must receive and calculate block rewards, the reward address of the CNv3 must be set to PD. If validator deploys multiple CNv3s to use both initial lockup and PD, the reward address for all CNv3s must be PD (i.e., the reward for initial lockup is also sent to PD).
When block reward is auto-compounding, the commission is calculated and paid automatically.
Since PD is a type of token contract, its name and symbol will be determined as follows:
- Name:
{gcName} Public Delegated KLAY(ex.KF Public Delegated KLAY) - Symbol:
{gcName}-pdKLAY(ex.KF-pdKLAY)
Interface
pragma solidity 0.8.25;
import "../CnV3/ICnStakingV3.sol";
import "./IKIP163.sol";
interface IPublicDelegation is IKIP163 {
/* ========== STRUCT ========== */
struct PDConstructorArgs {
address owner;
address commissionTo;
uint256 commissionRate;
string gcName;
}
/* ========== ENUM ========== */
/// @dev Current state of the withdrawal request
enum WithdrawalRequestState {
Undefined,
Requested,
Withdrawable,
Withdrawn,
PendingCancel,
Canceled
}
/* ========== EVENTS ========== */
// Initialization
event DeployContract(string _contractType, address _baseCnStakingV3, PDConstructorArgs _pdArgs);
// Operations
event UpdateCommissionTo(address indexed _prevCommissionTo, address indexed _commissionTo);
event UpdateCommissionRate(uint256 indexed _prevCommissionRate, uint256 indexed _commissionRate);
event SendCommission(address indexed _commissionTo, uint256 _commission);
// Staking
event Staked(address indexed _user, uint256 _assets, uint256 _shares);
event Redeemed(address indexed _user, address indexed _recipient, uint256 _assets, uint256 _shares);
event Redelegated(address indexed _user, address indexed _targetCnV3, uint256 _assets);
event RequestWithdrawal(
address indexed _user,
address indexed _recipient,
uint256 indexed _requestId,
uint256 _assets
);
event RequestCancelWithdrawal(address indexed _user, uint256 indexed _requestId);
event Claimed(address indexed _user, uint256 indexed _requestId);
/* ========== CONSTANT/IMMUTABLE GETTERS ========== */
function MAX_COMMISSION_RATE() external pure returns (uint256);
function COMMISSION_DENOMINATOR() external pure returns (uint256);
function CONTRACT_TYPE() external pure returns (string memory);
function VERSION() external pure returns (uint256);
function baseCnStakingV3() external view returns (ICnStakingV3);
/* ========== OPERATION FUNCTIONS ========== */
function updateCommissionTo(address _commissionTo) external;
function updateCommissionRate(uint256 _commissionRate) external;
/* ========== PUBLIC FUNCTIONS ========== */
// Staking
function stake() external payable;
function stakeFor(address _recipient) external payable; // Defined in IKIP163
receive() external payable;
// Withdrawal
function withdraw(address _recipient, uint256 _assets) external;
function redeem(address _recipient, uint256 _shares) external;
function cancelApprovedStakingWithdrawal(uint256 _requestId) external;
function claim(uint256 _requestId) external;
// Redelegation
function redelegateByAssets(address _targetCnV3, uint256 _assets) external;
function redelegateByShares(address _targetCnV3, uint256 _shares) external;
// Sweep
function sweep() external;
/* ========== PUBLIC VIEWS ========== */
function commissionTo() external view returns (address);
function commissionRate() external view returns (uint256);
function userRequestIds(address _owner, uint256 _index) external view returns (uint256);
function requestIdToOwner(uint256 _requestId) external view returns (address);
function getCurrentWithdrawalRequestState(uint256 _requestId) external view returns (WithdrawalRequestState);
function getUserRequestCount(address _owner) external view returns (uint256);
function getUserRequestIdsWithState(
address _owner,
WithdrawalRequestState _state
) external view returns (uint256[] memory);
function getUserRequestIds(address _owner) external view returns (uint256[] memory);
function maxRedeem(address _owner) external view returns (uint256);
function maxWithdraw(address _owner) external view returns (uint256);
function reward() external view returns (uint256); // Defined in IKIP163
function totalAssets() external view returns (uint256);
function convertToShares(uint256 _assets) external view returns (uint256);
function convertToAssets(uint256 _shares) external view returns (uint256);
function previewDeposit(uint256 _assets) external view returns (uint256);
function previewWithdraw(uint256 _assets) external view returns (uint256);
function previewRedeem(uint256 _shares) external view returns (uint256);
}
Constants
The PublicDelegation has constants related to commission.
MAX_COMMISSION_RATE: Max commission rate. It will be 10,000. (= 100%)COMMISSION_DENOMINATOR: Commission denominator. It will be 10,000.
Methods
All math for managing a user’s staking follows ERC4626 standard. Note that PD isn’t based on ERC20 assets, but native KLAY.
totalAssets(): Total assets managed by PD. It contains reward.maxRedeem(address owner): Max reedeemable shares of owner.maxWithdraw(address owner): Max withdrawable KLAY of owner.convertToAssets(uint256 shares): Expected KLAY when convert shares.previewDeposit(uint256 assets): Expected shares when deposit assets of KLAY.previewWithdraw(uint256 assets): Expected shares to withdraw assets of KLAY.previewRedeem(uint256 shares): Expected KLAY when redeem shares.
To enable auto-compounding, PD stakes cumulative KLAY rewards to CNv3 automatically when the below functions are called or call sweep function explicitly.
function updateCommissionTo(address _commissionTo);
It updates commission receiver address of PD. Previously accumulated commission must go to previous commission receiver.
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if caller is not an owner.
The function emits UpdateCommissionTo event.
function updateCommissionRate(uint256 _commissionRate);
It updates commission rate of PD. Previously accumulated rewards must follow previous commission rate.
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if caller is not an owner.
- The function MUST revert if
_commissionRateis higher thanMAX_COMMISSION_RATE.
The function emits UpdateCommissionRate event.
function stake() payable;
function stakeFor(address _recipient) payable;
Call delegate with msg.value to CNv3 internally. It must mint corresponding shares to user. stakeFor is used when msg.sender != _recipient.
| User gives | User receives |
|---|---|
KLAY |
previewDeposit(KLAY): Floored amount of shares (pdKLAY) |
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if user would receive 0 shares.
- The function MUST revert if delegate call reverts.
The function emits Staked event.
function withdraw(address _recipient, uint256 _assets);
function redeem(address _recipient, uint256 _shares)
Call approveStakingWithdrawal to CNv3 internally. It must burn corresponding shares of user. User will use withdraw to withdraw the exact amount of KLAY, otherwise use redeem to withdraw the exact amount of shares. Note that user must use redeem to withdraw all the KLAY because total withdrawable KLAY is changed every block (1 second).
User gives (pdKLAY) |
User will receive (7-day lockup) | |
|---|---|---|
withdraw(recipient, KLAY) |
previewWithdraw(KLAY): Ceiled amount of shares to withdraw KLAY |
KLAY |
redeem(recipient, shares) |
shares |
previewRedeem(shares): Floored amount of KLAY |
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if user requests to withdraw 0 KLAY.
- The function MUST revert if user withdraws more than staked.
- The function MUST revert if
approveStakingWithdrawalcall reverts.
The functions emit RequestWithdrawal event.
function cancelApprovedStakingWithdrawal(uint256 _requestId);
Call cancelApprovedStakingWithdrawal to CNv3 internally. User’s shares must be revived accordingly. Note that KLAY in withdrawal requests didn’t receive any rewards.
| User gives | User receives |
|---|---|
| - | previewDeposit(KLAY in withdrawal request): Floored amount of shares |
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if a user attempts to withdraw another user’s request.
- The function MUST revert if
cancelApprovedStakingWithdrawalcall reverts.
The function emits RequestCancelWithdrawal event.
function claim(uint256 _requestId);
Calls withdrawApprovedStaking to CNv3 internally. If the withdrawal was canceled, it must revive user’s shares accordingly. Note that KLAY in withdrawal requests didn’t receive any rewards.
| User gives | User receives | |
|---|---|---|
| Claim success | - | KLAY in withdrawal request |
| Claim failure | - | previewDeposit(KLAY in withdrawal request): Floored amount of shares |
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if a user attempts to claim another user’s request.
- The function MUST revert if
withdrawApprovedStakingcall reverts.
The function emits Claimed if withdrew successfully.
function redelegateByAssets(address _targetCnV3, uint256 _assets);
function redelegateByShares(address _targetCnV3, uint256 _shares);
Call redelegate to CNv3 internally. It must burn corresponding shares of users. User will use byAssets to redelegate the exact amount of KLAY, otherwise use byShares to redelegate the exact amount of shares. Note that user must use byShares to redelegate all the KLAY same reason as redeem. User must receive the corresponding shares by PD connected to targetCNv3. In below tables, $\color{blue}{blue}$ is for target, while $\color{red}{red}$ is from.
| User gives | User receives | |
|---|---|---|
redelegateByAssets(target, KLAY) |
$\color{red}{previewWithdraw(KLAY)}$: Ceiled amount of shares to redelegate KLAY | $\color{blue}{previewDeposit(KLAY)}$: Floored amount of shares |
redelegateByShares(target, shares) |
shares |
$\color{blue}{previewDeposit(KLAY)}$: Floored amount of shares, where KLAY is $\color{red}{previewRedeem(shares)}$ |
The function validates the following requirement(s):
- The function MUST revert if
_targetCnV3isn’t a valid CNv3 staking contract. - The function MUST revert if current CNv3 doesn’t allow redelegation.
- The function MUST revert if a user redelegates more KLAY than staked.
- The function MUST revert if a user redelegates 0 KLAY.
- The function MUST revert if
redelegatecall reverts.
The functions emit Redelegated event.
Core Logic
From FORK_BLOCK, the staking information for block N will be recorded in block N-1 instead of CalcStakingBlockNumber(N).
Parameters
| Constant | Value |
|---|---|
FORK_BLOCK |
TBD |
// In staking_manager.go
func GetStakingInfo(blockNum uint64) *StakingInfo {
stakingBlockNumber := blockNum
var stakingInfo *StakingInfo
if isForkBlockEnabled(blockNum) {
// After `FORK_BLOCK`, staking information for block `N` will be recorded in block `N-1`.
if blockNum > 0 {
stakingBlockNumber--
}
stakingInfo = GetStakingInfoForForkBlock(stakingBlockNumber)
} else {
// Before `FORK_BLOCK`, staking information for block `N` will be recorded in `CalcStakingBlockNumber(N)`.
stakingBlockNumber = params.CalcStakingBlockNumber(blockNum)
stakingInfo = GetStakingInfoOnStakingBlock(stakingBlockNumber)
}
return stakingInfo
}
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
GetStakingInfo(blockNum) |
Returns staking information needed to handle block blockNum. |
GetStakingInfoForForkBlock(blockNum) |
Returns staking information at block blockNum. If blockNum is before FORK_BLOCK - 1, return nil. |
GetStakingInfoOnStakingBlock(blockNum) |
Returns staking information at staking block blockNum. If blockNum is not a staking interval block nor after FORK_BLOCK, return nil. |
Rationale
Non-transferable shares in PublicDelegation
Originally, the shares minted by PublicDelegation is based on ERC4626, one of ERC20 extensions. It means shares will be utilized as a ERC20 token (e.g., Liquidity Pool, Collaterals). This is of course a common use cases on many blockchains; LST. However, since different LSTs are issued by each GC, which causes significant liquidity fragmentation. Therefore, although shares are not transferable in this KIP, Klaytn will keep considering ways to activate staked KLAY while preventing liquidity fragmentation.
Initial lockup and public delegation are mutually exclusive
All delegations must be through PublicDelegation if enabled. However, it conflicts with the existing initial lockup feature from CnStakingV2 because the initial lockup is staked directly into CnStakingV3 without PublicDelegation. To solve this issue, public delegation and initial lockup must be set to mutually exclusive. However, if both features must be used, there are alternative ways to achieve it:
- Deposit initial lockup through
PublicDelegationand implement additional logic for initial lockup (setup unlock time and amounts) - Maintain current initial lockup implementation. In
PublicDelegation, calculate the shares considering the initial lockup of CnStakingV3.
First approach needs additional implementation in PD only for initial lockup. This raises the question of whether it’s reasonable for PD to consider initial lockup. Developing an independent lockup contract for initial lockup is possible, but this causes additional security and maintenance issues.
The second approach makes PD logic more complicated. PD has to read the state of the initial lockup every time and make calculations, which is a permanent cost increase.
Overall, it’s determined that initial lockup and PD are best used in CNv3 where they are mutually exclusive and independent.
Backward Compatibility
The existing CNv1 and CNv2 and previous custom public delegation services will still be available. However, it is strongly recommended to deploy CNv3 for new GCs and gradually move to CNv3 for original GCs.
Security Considerations
ERC4626 Inflation Attack
This is fundamentally due to that when using ERC20 as a base asset, contract cannot prevent tokens from being deposited directly into it. This only increases the underlying asset without issuing any shares, and can result in zero shares for other users to receive. However, since the PD in this is based on the KLAY, we can control all KLAY inflows by fallback.
Implementation
TBA
References
Copyright
Copyright and related rights waived via CC0.